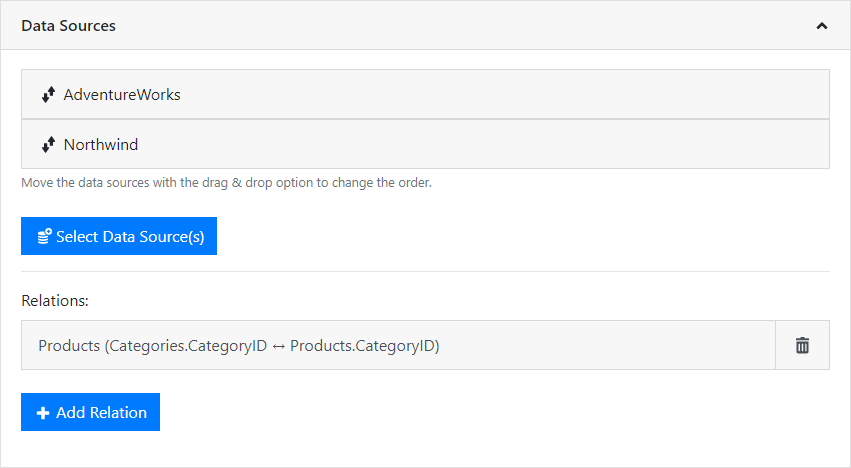
In addition to the possibility to define further relations within the same SQL data source (see section SQL databases), you can also define relations between different data sources, e.g. CSV file to SQL server and use them accordingly in the designer.
The relations between different data sources are defined individually for each report template. To do this, first select the required data sources and then supplement the required relations between these data sources.

Figure 2.22: Settings for a scheduled report
1. Choose "Add Relation" and enter a table alias (relation name). This name is displayed below the 1:n linked child table beneath the parent table in the Designer.
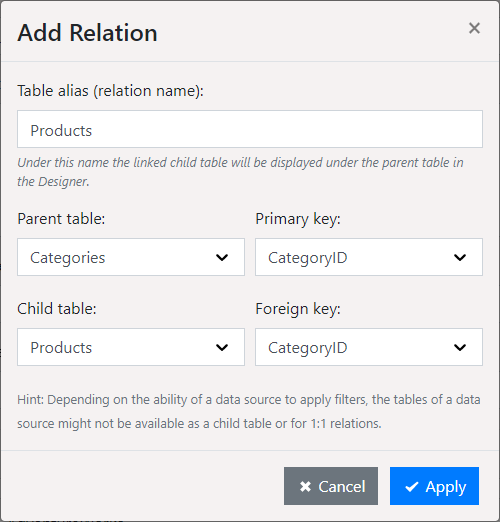
Figure 2.23: Define relations
2. Choose the parent table and the primary key field.
3. Chose the child table and the foreign key field that corresponds to the primary key of the parent table.
4. Relations can also be established with a compound key. The assignment (linking) of data records takes place when all fields match. Define one via "Add". If there are several entries in the assignments, a compound primary key is created. With a simple primary key, the list of assignments has only one entry.
5. Relations can not be defined arbitrarily, only data sources with filterable tables are available as child table.
▪ Filterable: All SQL databases, OData, ODBC, OLE DB, MongoDB, Cassandra, Salesforce
▪ Only filterable with in-memory option: CSV, Excel
▪ Not filterable: REST, JSON, XML, CouchDb, Google Analytics, Google BigQuery, Google Spreadsheet
Tables from, for example, a XML data source are not offered in the selection list for the child table. A non-filterable table as a parent table is possible, but the designer does not have the usual 1: 1 relations from the child to the parent table.